Android Handler模型
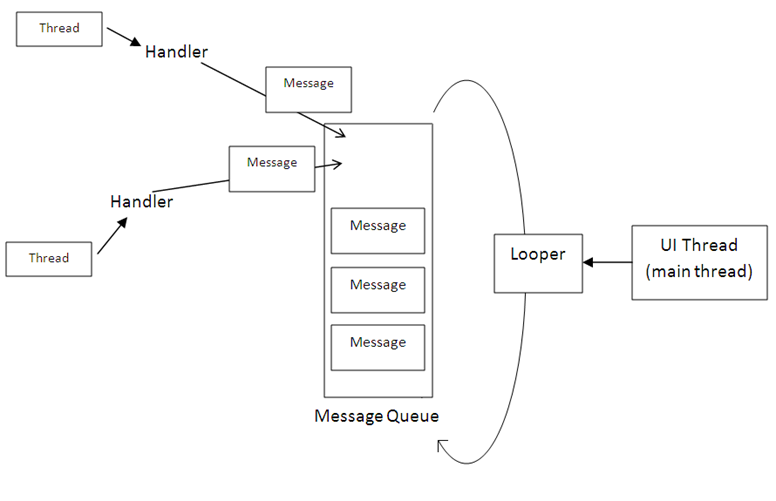
Message: 消息,其中包含了消息ID,消息处理对象以及处理的数据等,由MessageQueue统一列队,终由Handler处理。
Handler: 处理者,负责Message的发送及处理。使用Handler时,需要实现handleMessage(Message msg)方法来对特定的Message进行处理,例如更新UI等。
MessageQueue: 消息队列,用来存放Handler发送过来的消息,并按照FIFO规则执行。当然,存放Message并非实际意义的保存,而是将Message以链表的方式串联起来的,等待Looper的抽取。
Looper: 消息泵,不断地从MessageQueue中抽取Message执行。因此,一个MessageQueue需要一个Looper。
Thread: 线程,负责调度整个消息循环,即消息循环的执行场所。
源码分析
真正对应应用进程的不是Application而是ActivityThread。 每个应用程序都以ActivityThread.main()为入口进入到消息循环处理。对于一个进程来讲,我们需要这个闭合的处理框架。
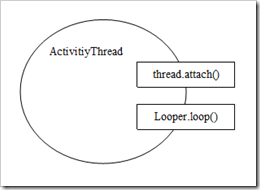
1 | public static final void main(String[] args) { |